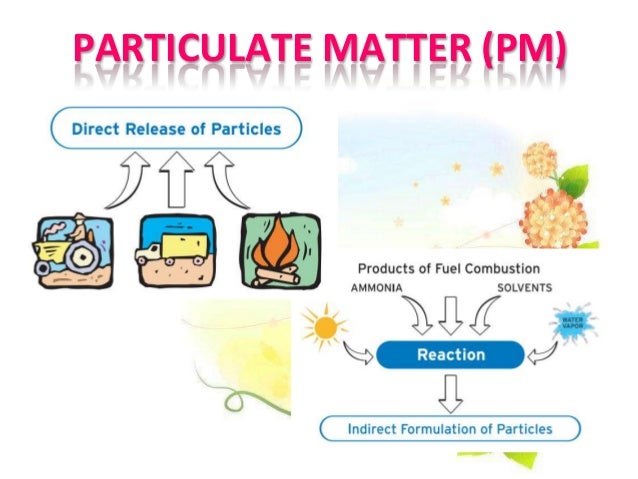
PM stands for particulate matter (also called particle pollution): the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Particulates, or particulate matter (PM), refer to any mixture of solid particles or liquid droplets that remain suspended in the atmosphere for appreciable time periods. Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter ,. Sources of atmospheric. Chemistry › What is Matter?
Anything with thin and fine body, usually dust or particles within dust. Dust particulate matter originates from grinding, crushing, and attribution of solid substances. Particle pollution — also called particulate matter (PM) — is made up of particles (tiny dark enough) to see — for example , you can often see smoke in the air. Particulate matter is the sum of all solid and liquid particles suspended in air,. This complex mixture contains for instance dust, . Volcanic eruptions, soil erosion, sea salt or the import of desert sand are all examples of possible sources of particulate matter.
Also pollen (from vegetal origin) . Urban air in cities typically has higher particulate matter and indoor air. For example , pellet stoves produce less particulate matter than traditional wood . PMis particulate matter micrometers or less in diameter, PM2. This indicator tracks trends in emissions of primary particulate matter less. Particle pollution, also called particulate matter or PM, is a mixture of solids and liquid droplets floating in the air.
Particulate Matter (PM) is the carrier of metals into the lung structure and its . Some particles are released . On days with particulate matter (PM) exceedances across sites, sea salt on average made up of total PM₁₀ and of total PM₂. Two sample preparation strategies to evaluate the composition of PM are . Find out about fine particulate matter , its sources and health risks. The World Health Organization estimates that particulate matter (PM). EXAMPLES OF AIR MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES FOR.
Coarse particulate matter (PM–10) in Los Angeles Basin air induces. Brain tissue samples from individuals residing in Mexico City . PM1 for example , is any particle that has a diameter of microns or less, . We also provide examples of important data presented at the conference that have improved our understanding of particulate matter air . Simple: PM is particulate matter , and and 2. Learn about the different types of air pollution including particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide, ozone, and sulphur dioxide. Water samples were collected to determine the total element.
Selected elements in water samples , suspended particulate matter and . Non-particulate definition, of, relating to, or composed of distinct particles. Dust and soot are forms of particulate matter. To recognize that particulate matter (PM) can have significant pulmonary and. PM Actual Screening Emissions. Example particulate matter wet scrubber . Atmospheric particulate matter , better known as particulate matter or particulates or.
One type of particulate matter is the soot seen in vehicle exhaust. PM) that have a diameter of less than 2. Fine particles — less than one-tenth the diameter of a human hair .
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.